Project Overview
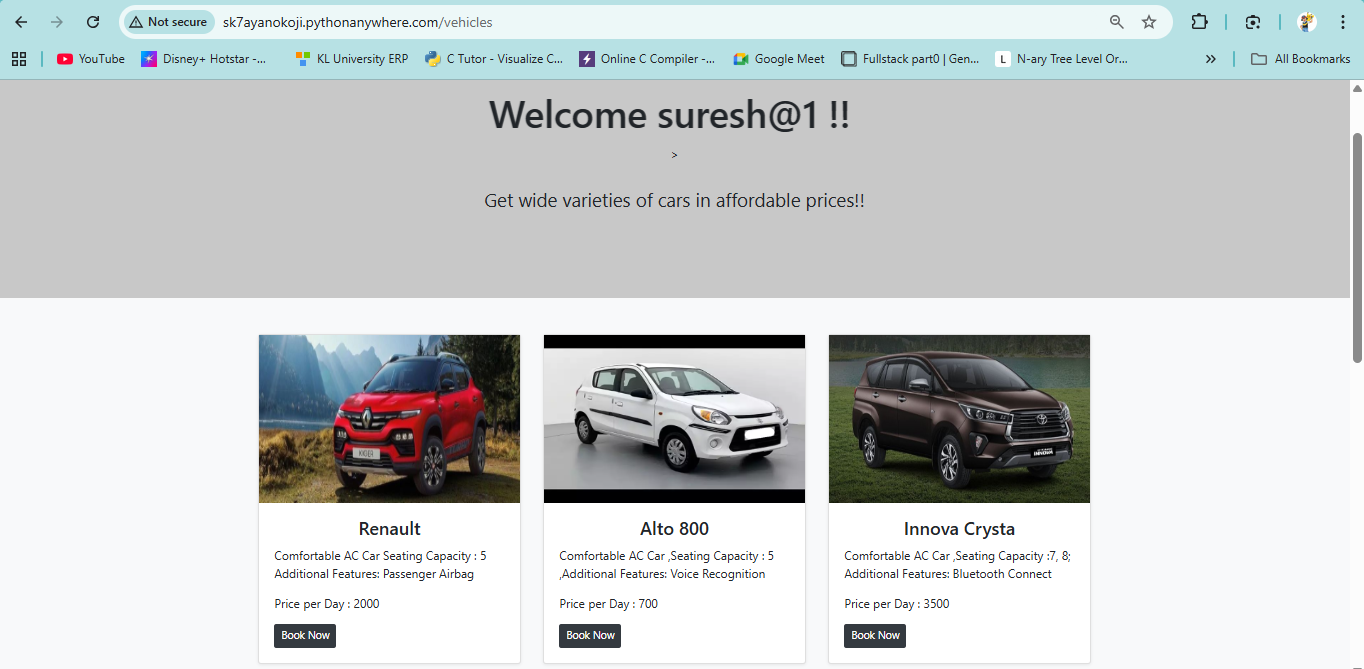
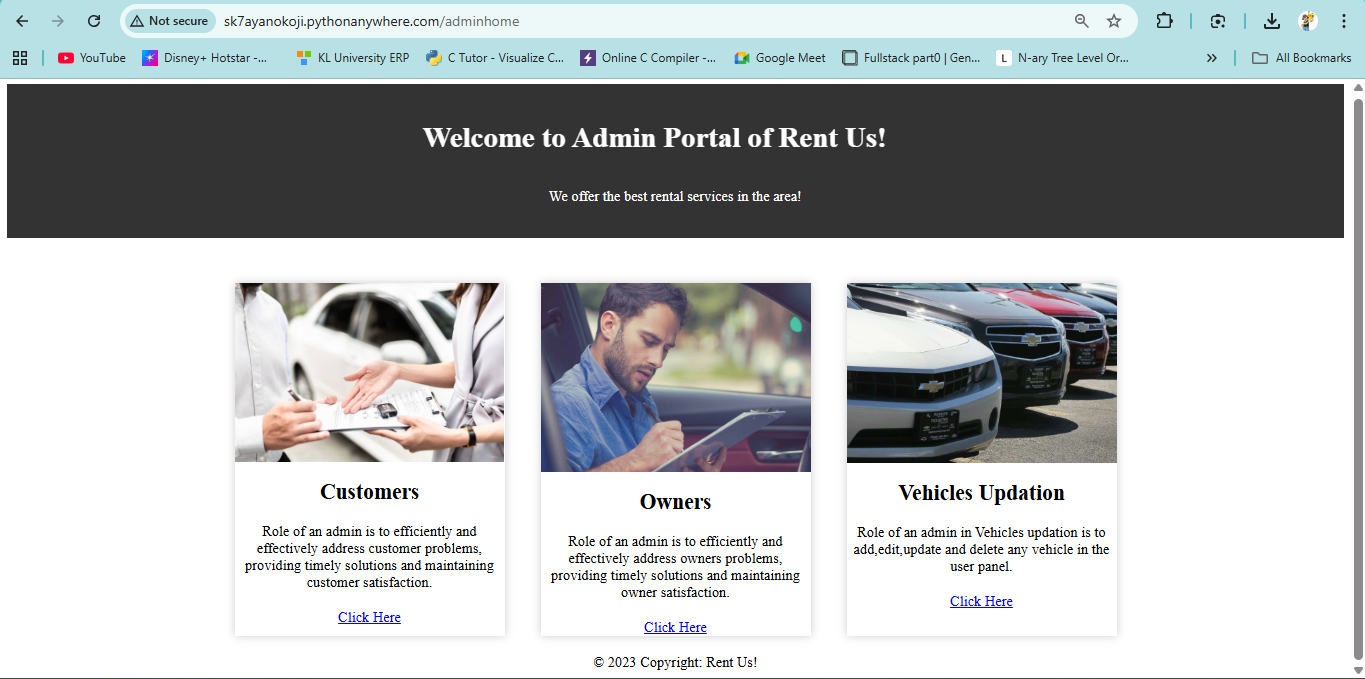
Rent Us! is a web-based rental management platform built with Django, designed to simplify renting vehicles like bikes, vans, and cars. It offers a user-friendly interface for users to browse, rent, and pay for vehicles, while owners can list their vehicles and track rentals. Admins have access to comprehensive dashboards showing rental histories, user activity, and owner profits.
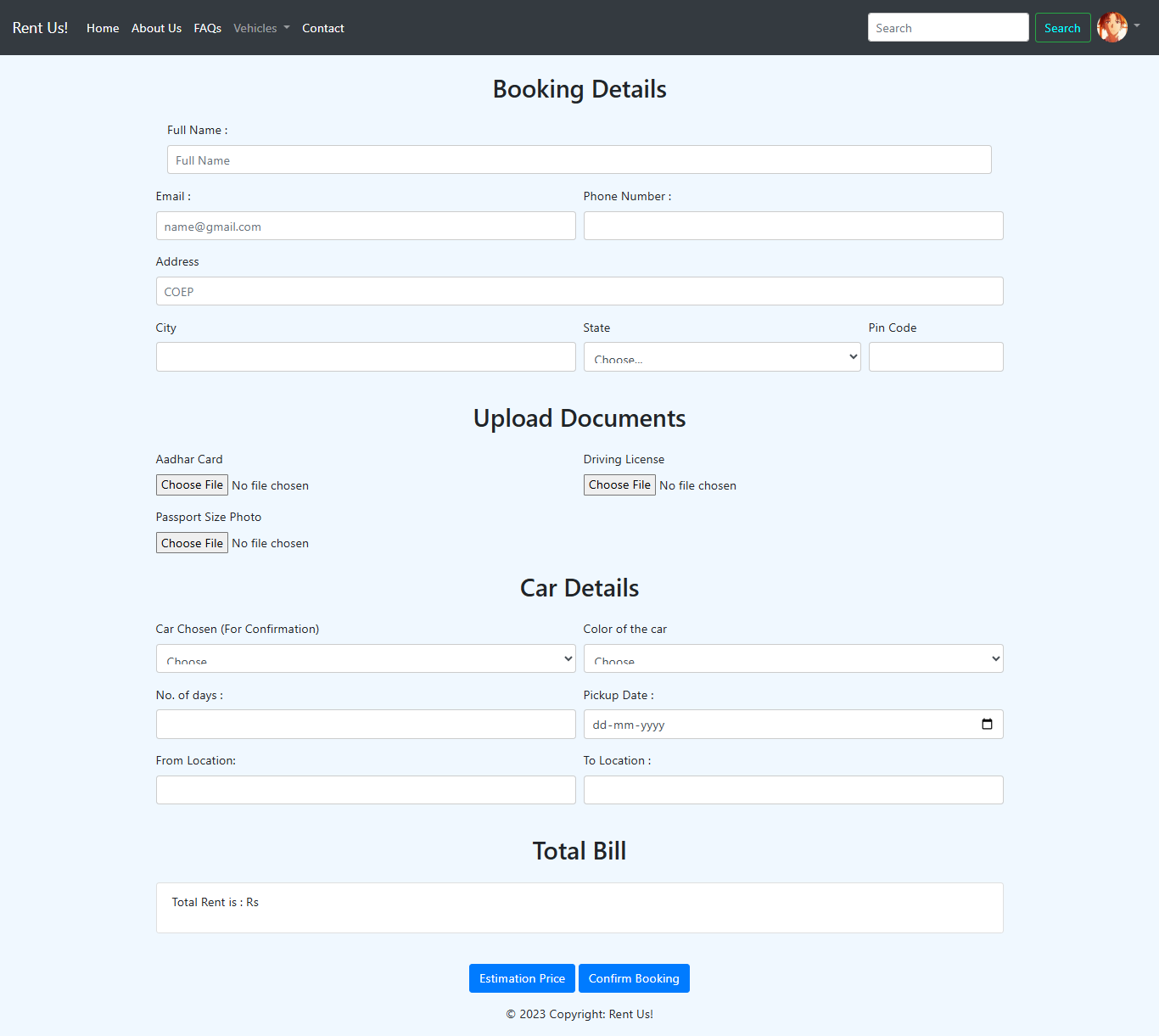
Key features include user authentication, role-based access (User, Owner, Admin), CRUD operations for managing vehicles and users, payment integration, and a contact system for resolving disputes. The app uses SQLite locally and MySQL for deployment on PythonAnywhere, ensuring scalability and responsiveness across devices with Bootstrap-enhanced styling.
Technical Highlights
Performance Optimization
- Efficient Django ORM queries
- Lightweight SQLite/MySQL backend
- Responsive Bootstrap styling
Security Features
- Robust user authentication
- Role-based access control
- Input validation mechanisms
Project Gallery
Frequently Asked Questions
My team designed Rent Us! by leveraging Django’s robust framework to create a modular, role-based system for users, owners, and admins. We used Django’s authentication system for secure login and role management, defining models for vehicles (bikes, vans, cars), rentals, and users, with MySQL for production and SQLite for development. The frontend was built with HTML, CSS, and Bootstrap for responsive layouts, enhanced by JavaScript for dynamic interactions like price calculations based on rental days.
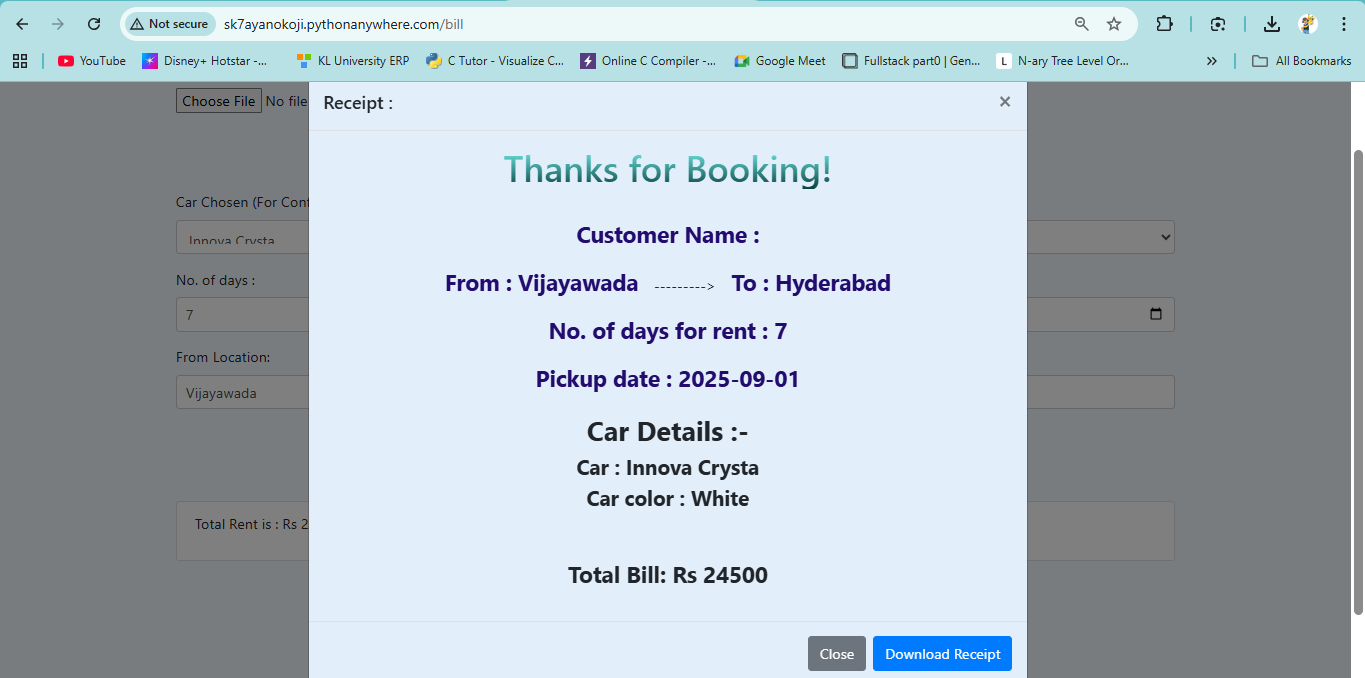
CRUD operations were implemented via Django views and templates, while admin dashboards used Django’s admin interface to display rental histories and profits. Payment integration was added using a third-party API (assumed, as not specified in the code), and a contact form was included to handle disputes, ensuring a seamless experience across all user roles.
The main challenge in Rent Us! was managing reliable database connections across MySQL, SQLite, MongoDB, and PostgreSQL, as varying configurations caused connection failures and disrupted rental and user data access. We created a backup project to test configurations, standardized on MySQL for production and SQLite for development, and used Django’s settings module to simplify switching, testing thoroughly to ensure stable integration.
Another issue was Stripe payment integration, where API errors and incomplete transaction flows blocked secure payments. We pivoted to a manual payment system using HTML input forms, securely storing details in Django’s admin database with validation, maintaining functionality while planning to revisit Stripe with better testing later.
To ensure scalability, we used Django’s efficient ORM for optimized database queries and switched to MySQL for production on PythonAnywhere, which handles larger datasets better than SQLite. The modular design with separate models for users, vehicles, and rentals allows easy scaling for more vehicle types or users, while Bootstrap ensures a responsive UI for various devices.
For security, we implemented Django’s authentication system with password hashing, role-based access to restrict actions (e.g., only admins view profit data), and input validation to prevent injection attacks.
